[UESTC-信软] iCoding F2 Answer
字符串
块链串
块链串定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| #define BLOCK_SIZE 4
#define BLS_BLANK '#'
typedef struct _block {
char ch[BLOCK_SIZE];
struct _block *next;
} Block;
typedef struct {
Block *head;
Block *tail;
int len;
} BLString;
void blstr_init(BLString *T) {
T->len = 0;
T->head = NULL;
T->tail = NULL;
}
|
这些定义已包含在头文件 dsstring.h 中,请实现块链串的子串查找操作:
1
| bool blstr_substr(BLString src, int pos, int len, BLString *sub);
|
- src: 为要查找的字符串
- pos: 为子串开始的下标
- len: 为子串的长度
- sub: 在函数调用运行前指向一个已经初始化好的空串,在函数返回时,sub 指向串 src 从第 pos 个字符起长度为 len 的子串
- 函数查找成功返回 true,参数不正确返回 false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "dsstring.h"
bool blstr_substr(BLString src, int pos, int len, BLString *sub)
{
if(len <= 0)
return false;
int index = pos / BLOCK_SIZE, offset = pos % BLOCK_SIZE;
Block *pBh = src.head;
int now = 0;
while (now++ < index)
pBh = pBh->next;
int counts = 0, counts2 = offset;
Block *newBlock = NULL;
while (pBh && counts < len )
{
if (counts + pos >= src.len)
break;
if (counts % BLOCK_SIZE == 0)
{
newBlock = (Block *)malloc(sizeof(Block));
if (newBlock == NULL)
return false;
if (sub->head)
{
sub->tail->next = newBlock;
sub->tail = sub->tail->next;
}
else
{
sub->head = sub->tail = newBlock;
}
sub->tail->next = NULL;
}
newBlock->ch[counts++ % BLOCK_SIZE] = pBh->ch[counts2++ % BLOCK_SIZE];
if (counts2 % BLOCK_SIZE == 0)
{
pBh = pBh->next;
counts2 = 0;
}
}
while (counts % BLOCK_SIZE != 0)
{
newBlock->ch[counts % BLOCK_SIZE] = BLS_BLANK;
counts++;
}
sub->tail->next = NULL;
if (pos + len > src.len)
sub->len = src.len - pos;
else
sub->len = len;
return true;
}
|
串替换
不调用库函数,自己实现字符串替换操作,函数原型为:
1
| int str_replace(const char *in, char *out, int outlen, const char *oldstr, const char *newstr);
|
参数说明:
- in: 原始字符串,保持不变
- out: 存放替换结果的字符串
- outlen: out空间的大小
- oldstr: 要替换的旧字符串
- newstr: 替换成的新字符串
- 函数返回成功替换的次数,即有多少个子串被成功替换
在替换过程中,任何情况下所得字符串(及结束符)不应该超过 outlen,如果某次替换所得字符串的长度超过 outlen,则不进行这次替换操作,整个替换操作结束。如:
原始串为 “aaabbbccc”,outlen 为 14 , oldstr 为 “c”,newstr 为 “333” 时,两次替换后得 “aaabbb333333c”,此时字符串占用空间为 14 字节。
如果再进行替换,则会超出 out 所占用的空间,所以停止替换操作。
此时函数应该返回 2, out 指向的串为 “aaabbb333333c”
再如:原始串为 “aaabbbccc”,outlen 为10, oldstr 为 “b”,newstr 为 “123456”,进行替换后所得的串长度为 14,与结束符一共占 15 个字节,超过 outlen 的 10 字节,此时不进行替换,函数应该返回 0。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| #include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "dsstring.h"
int str_len(const char* str) {
int length = 0;
while (str[length] != '\0')
length++;
return length;
}
int str_replace(const char *in, char *out, int outlen,
const char *oldstr, const char *newstr)
{
int replaceCounts = 0,
lenOfOldstr = str_len(oldstr),
lenOfNewstr = str_len(newstr);
int offset = 0, i = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < outlen; i++)
{
out[i] = '\0';
}
while (in[i] != '\0')
{
int match = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < lenOfOldstr; j++)
{
if (in[i + j] != oldstr[j])
{
match = 0;
break;
}
}
if (match && offset + str_len(in) - i - lenOfOldstr + lenOfNewstr < outlen)
{
for (int j = 0; j < lenOfNewstr; j++)
{
out[offset++] = newstr[j];
}
replaceCounts++;
i += lenOfOldstr;
}
else
{
if (offset >= outlen - 1)
return 0;
out[offset] = in[i];
offset++;
i++;
}
}
out[outlen] = '\0';
return replaceCounts;
}
|
串比较
不调用库函数,自己实现字符串的比较操作:该操作当比较的两个字符是都是字母,且两个字符互为大小写(如 a 和 A 、 e 和 E )时认为两个字符相同,否则不同,其比较结果按这两个字符的原值确定。函数的返回值规定如下:
- 返回值 < 0:第一个不匹配的字符在 ptr1 中的值低于 ptr2 中的值
- 返回值 == 0:两个字符串的内容相等
- 返回值 > 0:第一个不匹配的字符在 ptr1 中的值大于在 ptr2 中的值
函数原型如下:
1
| int str_compare(const char* ptr1, const char* ptr2);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "dsstring.h"
int str_len(const char *str)
{
int length = 0;
while (str[length] != '\0')
length++;
return length;
}
int str_compare(const char *ptr1, const char *ptr2)
{
int lenOfPtr1 = str_len(ptr1);
int lenOfPtr2 = str_len(ptr2);
int max = lenOfPtr1 >= lenOfPtr2 ? lenOfPtr1 : lenOfPtr2;
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++)
{
if (ptr1[i] == ptr2[i])
continue;
if (ptr1[i] < ptr2[i])
{
if (ptr1[i] >= 'A' && ptr1[i] <= 'Z' && (ptr2[i] - ptr1[i] == 32))
continue;
return ptr1[i] - ptr2[i];
}
if (ptr1[i] > ptr2[i])
{
if (ptr1[i] >= 'a' && ptr1[i] <= 'z' && (ptr1[i] - ptr2[i] == 32))
continue;
return ptr1[i] - ptr2[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
|
队列栈
栈 后缀表达式计算
请使用已定义好的栈完成后缀表达式计算:
- 如果是操作数,直接入栈
- 如果是操作符 op,连续出栈两次,得到操作数 x 和 y ,计算 x op y,并将结果入栈。
后缀表达式示例如下:
- 9 3 1 - 3 * + 10 2 / +
- 13 445 + 51 / 6 -
操作数、操作符之间由空格隔开,操作符有 +,-,*, /, **%**共 5 种符号,所有操作数都为整型。
栈的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #define Stack_Size 50
typedef struct{
ElemType elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}Stack;
bool push(Stack* S, ElemType x);
bool pop(Stack* S, ElemType *x);
void init_stack(Stack *S);
|
其中,栈初始化的实现为:
1
2
3
| void init_stack(Stack *S){
S->top = -1;
}
|
需要完成的函数定义为:
1
| int compute_reverse_polish_notation(char *str);
|
函数接收一个字符指针,该指针指向一个字符串形式的后缀表达式,函数返回该表达式的计算结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int compute_reverse_polish_notation(char *str)
{
Stack stack;
init_stack(&stack);
char *partStr = strtok(str, " ");
while (partStr)
{
if (isdigit(partStr[0]))
push(&stack, atoi(partStr));
else
{
int x, y;
pop(&stack, &y);
pop(&stack, &x);
switch (partStr[0])
{
case '+':
push(&stack, x + y);
break;
case '-':
push(&stack, x - y);
break;
case '*':
push(&stack, x * y);
break;
case '/':
push(&stack, x / y);
break;
case '%':
push(&stack, x % y);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
partStr = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
return stack.elem[stack.top];
}
|
队列 循环链表表示队列
假设以带头结点的循环链表表示队列,并且只设一个指针指向队尾元素结点(注意不设头指针),请完成下列任务:
队列初始化,成功返回真,否则返回假:
1
| bool init_queue(LinkQueue *LQ);
|
入队列,成功返回真,否则返回假:
1
| bool enter_queue(LinkQueue *LQ, ElemType x);
|
出队列,成功返回真,且 *x为出队的值,否则返回假
1
| bool leave_queue(LinkQueue *LQ, ElemType *x);
|
相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
| typedef struct _QueueNode {
ElemType data;
struct _QueueNode *next;
}LinkQueueNode, *LinkQueue;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
bool init_queue(LinkQueue *LQ)
{
*LQ = (LinkQueue)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
if (!LQ)
return false;
(*LQ)->next = *LQ;
return true;
}
bool enter_queue(LinkQueue *LQ, ElemType x)
{
LinkQueueNode *newQueueNode = (LinkQueueNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueueNode));
if (!newQueueNode)
return false;
newQueueNode->data = x;
newQueueNode->next = (*LQ)->next;
(*LQ)->next = newQueueNode;
(*LQ) = (*LQ)->next;
return true;
}
bool leave_queue(LinkQueue *LQ, ElemType *x)
{
if ((*LQ)->next == *LQ)
return false;
LinkQueueNode *firstNode = (*LQ)->next->next;
*x = firstNode->data;
(*LQ)->next->next = firstNode->next;
if (firstNode == *LQ)
*LQ = (*LQ)->next;
free(firstNode);
return true;
}
|
线性表
链表 合并
设线性表 A=(a1, a2,…,am),B=(b1, b2,…,bn),试写一个按下列规则合并 A、B 为线性表 C 的算法,使得:
- C= (a1, b1,…,am, bm, bm+1, …,bn) 当 m≤n 时;
或者
- C= (a1, b1,…,an, bn, an+1, …,am) 当 m>n 时。
线性表 A、B、C 均以单链表作为存储结构,且 C 表利用 A 表和 B 表中的结点空间构成。注意:单链表的长度值 m 和 n 均未显式存储。
函数的原型如下:
1
| void lnk_merge(LinkList A, LinkList B, LinkList C)
|
即将 A 和 B 合并为 C,其中 C 已经被初始化为空单链表
相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| struct _lnklist{
ElemType data;
struct _lnklist *next;
};
typedef struct _lnklist Node;
typedef struct _lnklist *LinkList;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
void lnk_merge(LinkList A, LinkList B, LinkList C)
{
Node *pA = A->next, *pB = B->next, *pC = C;
while (pA && pB)
{
pC->next = pA;
pA = pA->next;
pC = pC->next;
pC->next = pB;
pB = pB->next;
pC = pC->next;
}
while (pA)
{
pC->next = pA;
pC = pC->next;
pA = pA->next;
}
while (pB)
{
pC->next = pB;
pC = pC->next;
pB = pB->next;
}
pC->next = NULL;
}
|
链表 倒数查找
已知一个带有表头结点的单链表, 假设链表只给出了头指针 L 。
在不改变链表的前提下,请设计一个尽可能高效的算法,查找链表中倒数第 k 个位置上的结点( k 为正整数)。
函数原型为:
1
| int lnk_search(LinkList L, int k, ElemType* p_ele)
|
若查找成功,函数通过指针参数 p_ele 返回该结点 data 域的值,此时函数返回 1;
否则,函数返回 0 。
相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| struct _lnklist{
ElemType data;
struct _lnklist *next;
};
typedef struct _lnklist Node;
typedef struct _lnklist *LinkList;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
int lnk_search(LinkList L, int k, ElemType* p_ele) {
Node *p1 = L->next, *p2 = L->next;
int counts = 0;
while (p2->next)
{
if (counts++ > k)
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
*p_ele = p1->data;
return 1;
}
|
链表 删除范围内结点
已知线性表中的元素(整数)以值递增有序排列,并以单链表作存储结构。
试写一高效算法,删除表中所有大于 mink 且小于 maxk 的元素(若表中存在这样的元素),分析你的算法的时间复杂度。
链表结点定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| struct _lnklist{
ElemType data;
struct _lnklist *next;
};
typedef struct _lnklist Node;
typedef struct _lnklist *LinkList;
|
函数原型如下:
1
| void lnk_del_x2y(LinkList L, ElemType mink, ElemType maxk)
|
其中L指向链表的头结点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
void lnk_del_x2y(LinkList L, ElemType mink, ElemType maxk)
{
Node *pL = L, *temp = L->next;
while (pL->next && pL->next->data <= mink)
{
pL = pL->next;
}
temp = pL->next;
while (pL->next && pL->next->data < maxk)
{
pL->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
temp = pL->next;
}
}
|
顺序表 数据调整
已知顺序表 L 中的数据元素类型为 int 。
设计算法将其调整为左右两部分,左边的元素(即排在前面的)均为奇数,右边所有元素(即排在后面的)均为偶数,并要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n) ,空间复杂度为 O(1) 。
函数原型如下:
1
| void odd_even(SeqList *L);
|
相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| struct _seqlist{
ElemType elem[MAXSIZE];
int last;
};
typedef struct _seqlist SeqList;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
void odd_even(SeqList *L)
{
int left = 0,
right = L->last,
temp = 0;
while (left < right)
{
if (L->elem[left] % 2 == 0 && L->elem[right] % 2 != 0)
{
temp = L->elem[right];
L->elem[right] = L->elem[left];
L->elem[left] = temp;
right--;
left++;
}
if (L->elem[left] % 2 != 0)
left++;
if (L->elem[right] % 2 == 0)
right--;
}
}
|
顺序表 删除重复
编写算法,在一非递减的顺序表 L 中,删除所有值相等的多余元素。要求时间复杂度为 **O(n)**,空间复杂度为 **O(1)**。
函数原型如下:
1
| void del_dupnum(SeqList *L)
|
相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| struct _seqlist{
ElemType elem[MAXSIZE];
int last;
};
typedef struct _seqlist SeqList;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
void del_dupnum(SeqList *L)
{
int map[1001] = {0},
i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < L->last + 1; j++)
{
if (map[L->elem[j]] == 0)
{
map[L->elem[j]] = 1;
L->elem[i++] = L->elem[j];
}
}
L->last = i - 1;
}
|
顺序表 删除指定范围
设计一个高效的算法,从顺序表 L 中删除所有值介于 x 和 y 之间(包括 x 和 y )的所有元素(假设 y>=x ),要求时间复杂度为 O(n) ,空间复杂度为 O(1) 。
函数原型如下:
1
| void del_x2y(SeqList *L, ElemType x, ElemType y);
|
相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| struct _seqlist{
ElemType elem[MAXSIZE];
int last;
};
typedef struct _seqlist SeqList;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
void del_x2y(SeqList *L, int x, int y)
{
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < L->last + 1; j++)
{
if (L->elem[j] < x || L->elem[j] > y)
{
L->elem[i++] = L->elem[j];
}
}
L->last = i - 1;
}
|
图的存储
邻接矩阵
试在邻接矩阵存储结构上实现图的基本操作 matrix_insert_vertex 和matrix_insert_arc,相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| typedef int VertexType;
typedef enum{
DG, UDG
}GraphType;
typedef struct{
VertexType vertex[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int arcs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphType type;
}MatrixGraph;
int matrix_locate_vertex(MatrixGraph *MG, VertexType vex);
bool matrix_insert_vertex(MatrixGraph *G, VertexType v);
bool matrix_insert_arc(MatrixGraph *G, VertexType v, VertexType w);
|
当成功插入顶点或边时,函数返回 true,否则(如顶点或边已存在、插入边时顶点 v 或 w 不存在)返回 false。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| #include <stdio.h>
#include "graph.h"
bool matrix_insert_vertex(MatrixGraph *G, VertexType v)
{
if (G->vexnum < MAX_VERTEX_NUM)
if (matrix_locate_vertex(G, v) == -1)
{
G->vertex[G->vexnum++] = v;
for (int i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
G->arcs[i][G->vexnum - 1] = G->arcs[G->vexnum - 1][i] = 0;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool matrix_insert_arc(MatrixGraph *G, VertexType v, VertexType w)
{
int vLoc = matrix_locate_vertex(G, v);
int wLoc = matrix_locate_vertex(G, w);
if (vLoc != -1 && wLoc != -1 && G->arcs[vLoc][wLoc] != 1)
{
G->arcs[vLoc][wLoc] = 1;
if (G->type == UDG)
G->arcs[wLoc][vLoc] = 1;
G->arcnum++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
邻接表1
试在邻接表存储结构上实现图的基本操作 insert_vertex 和 insert_arc,相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| typedef int VertexType;
typedef enum{
DG, UDG
}GraphType;
typedef struct ArcNode
{
int adjvex;
InfoPtr *info;
struct ArcNode *nextarc;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode
{
VertexType data;
ArcNode *firstarc;
}VNode;
typedef struct
{
VNode vertex[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphType type;
}ListGraph;
int locate_vertex(ListGraph* G, VertexType v);
bool insert_vertex(ListGraph *G, VertexType v);
bool insert_arc(ListGraph *G, VertexType v, VertexType w);
|
当成功插入顶点或边时,函数返回 true,否则(如顶点或边已存在、插入边时顶点 v 或 w 不存在)返回 false。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "graph.h"
bool insert_vertex(ListGraph *G, VertexType v)
{
if (G->vexnum < MAX_VERTEX_NUM)
if (locate_vertex(G, v) == -1)
{
VNode newNode = {v, NULL};
G->vertex[G->vexnum++] = newNode;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool insert_arc(ListGraph *G, VertexType v, VertexType w)
{
int vLoc = locate_vertex(G, v);
int wLoc = locate_vertex(G, w);
if (vLoc == -1 || wLoc == -1)
return false;
ArcNode *vArcNode = G->vertex[vLoc].firstarc;
while (vArcNode)
{
if (vArcNode->adjvex == wLoc)
return false;
vArcNode = vArcNode->nextarc;
}
ArcNode *newNode = (ArcNode *)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
if (newNode == NULL)
return false;
newNode->adjvex = wLoc;
newNode->nextarc = G->vertex[vLoc].firstarc;
G->vertex[vLoc].firstarc = newNode;
G->arcnum++;
return true;
}
|
邻接表2
试在邻接表存储结构上实现图的基本操作 del_vertex,相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| typedef int VertexType;
typedef enum{
DG, UDG
}GraphType;
typedef struct ArcNode{
int adjvex;
InfoPtr *info;
struct ArcNode *nextarc;
}ArcNode;
typedef struct VNode{
VertexType data;
ArcNode *firstarc;
}VNode;
typedef struct{
VNode vertex[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
int vexnum, arcnum;
GraphType type;
}ListGraph;
int locate_vertex(ListGraph *G, VertexType v);
bool del_vertex(ListGraph *G, VertexType v);
|
当成功删除顶点或边时,函数返回 true,否则(如顶点或边不存在、删除边时顶点 v 或 w 不存在)返回 false。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "graph.h"
bool del_vertex(ListGraph *G, VertexType v)
{
int vLoc = locate_vertex(G, v);
if (vLoc == -1)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
if (i == vLoc)
{
ArcNode *arcNode = G->vertex[vLoc].firstarc;
while (arcNode)
{
ArcNode *temp = arcNode;
arcNode = arcNode->nextarc;
free(temp);
G->arcnum--;
}
continue;
}
ArcNode *prev = NULL;
ArcNode *arcNode = G->vertex[i].firstarc;
while (arcNode)
{
if (arcNode->adjvex == vLoc)
{
if (prev)
prev->nextarc = arcNode->nextarc;
else
G->vertex[i].firstarc = arcNode->nextarc;
free(arcNode);
G->arcnum--;
break;
}
prev = arcNode;
arcNode = arcNode->nextarc;
}
}
for (int i = vLoc; i < G->vexnum - 1; i++)
G->vertex[i] = G->vertex[i + 1];
G->vexnum--;
for (int i = 0; i < G->vexnum; i++)
{
ArcNode *arcNode = G->vertex[i].firstarc;
while (arcNode)
{
if (arcNode->adjvex > vLoc)
arcNode->adjvex--;
arcNode = arcNode->nextarc;
}
}
return true;
}
|
树二叉树
先序遍历
已知二叉树按照二叉链表方式存储,利用栈的基本操作写出先序遍历非递归形式的算法:
1
| void pre_order(BiTree root);
|
在遍历过程中,pre_order 函数需要调用 visit_node 函数来实现对结点的访问,该函数声明如下:
1
| void visit_node(BiTNode *node);
|
二叉树的相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node{
DataType data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
|
遍历所使用栈的相关操作如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #define Stack_Size 50
typedef BiTNode* ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}Stack;
void init_stack(Stack *S);
bool push(Stack* S, ElemType x);
bool pop(Stack* S, ElemType *px);
bool top(Stack* S, ElemType *px);
bool is_empty(Stack* S);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "bitree.h"
void pre_order(BiTree root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
Stack s;
init_stack(&s);
BiTree current = root;
push(&s, current);
while (!is_empty(&s))
{
pop(&s, ¤t);
visit_node(current);
if (current->right)
push(&s, current->right);
if (current->left)
push(&s, current->left);
}
}
|
路径
假设二叉树采用二叉链表方式存储, root 指向根结点,node 指向二叉树中的一个结点,编写函数 path,计算 root 到 node 之间的路径,(该路径包括 root 结点和 node 结点)。
path 函数声明如下:
1
| bool path(BiTNode* root, BiTNode* node, Stack* s);
|
其中,root 指向二叉树的根结点,node 指向二叉树中的另一结点,s 为已经初始化好的栈,该栈用来保存函数所计算的路径,如正确找出路径,则函数返回 true,此时 root 在栈底,node 在栈顶;如未找到,则函数返回 false, 二叉树的相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node{
DataType data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
|
栈的相关定义及操作如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #define Stack_Size 50
typedef BiTNode* ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}Stack;
void init_stack(Stack *S);
bool push(Stack* S, ElemType x);
bool pop(Stack* S, ElemType *px);
bool top(Stack* S, ElemType *px);
bool is_empty(Stack* S);
|
在提示中,树用缩进的形式展示
如二叉树 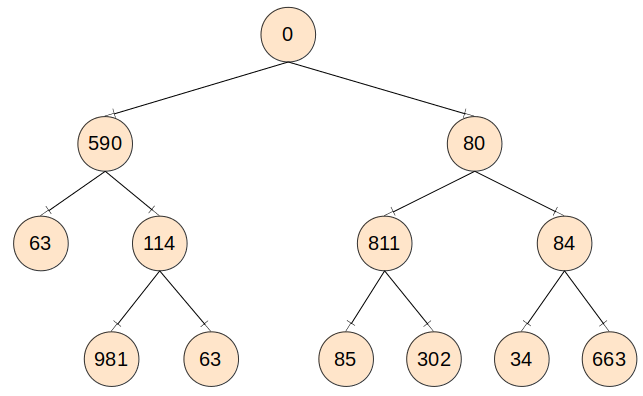 ,其缩进形式为:
,其缩进形式为: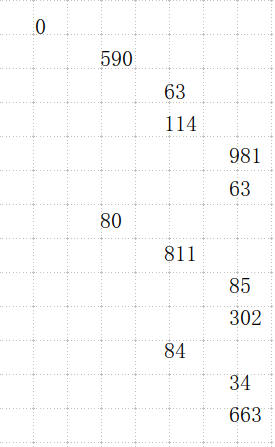 。
。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "bitree.h"
bool path(BiTNode *root, BiTNode *node, Stack *s)
{
if (root == NULL || node == NULL)
return false;
push(s, root);
if (root == node)
return true;
if (path(root->left, node, s) || path(root->right, node, s))
return true;
pop(s, &(s->elem[s->top]));
return false;
}
|
共同祖先
假设二叉树采用二叉链表方式存储, root 指向根结点,p 所指结点和 q 所指结点为二叉树中的两个结点,编写一个计算它们的最近的共同祖先,函数定义如下:
1
| BiTNode * nearest_ancestor(BiTree root, BiTNode *p, BiTNode *q);
|
其中 root 指向二叉树的根结点,p 和 q 分别指向二叉树中的两个结点。
提示:在完成本题时,可利用 path 函数获取 p 和 q 两个结点到根结点之间的路径,之后再计算两条公共路径得出最近的共同祖先。
path 函数及栈相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| bool path(BiTNode* root, BiTNode* node, Stack* s);
#define Stack_Size 50
typedef BiTNode* ElemType;
typedef struct{
ElemType elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
}Stack;
void init_stack(Stack *S);
bool push(Stack* S, ElemType x);
bool pop(Stack* S, ElemType *px);
bool top(Stack* S, ElemType *px);
bool is_empty(Stack* S);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "bitree.h"
void swap(Stack *p, Stack *q)
{
Stack tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
BiTNode *nearest_ancestor(BiTree root, BiTNode *p, BiTNode *q)
{
Stack sP, sQ;
init_stack(&sP);
init_stack(&sQ);
if (!path(root, p, &sP) || !path(root, q, &sQ))
return NULL;
if (sP.top < sQ.top)
swap(&sP, &sQ);
BiTree nodeP, nodeQ;
while (sP.top != sQ.top)
pop(&sP, &nodeP);
while (!is_empty(&sP) && !is_empty(&sQ))
{
pop(&sP, &nodeP);
pop(&sQ, &nodeQ);
if (nodeP == nodeQ)
return nodeP;
}
return NULL;
}
|
树转二叉树
使用队列,编写 transfrom 函数,将普通树转换成对应的二叉树。二叉树的相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Node{
DataType data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
|
普通树节点的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| #define MAX_CHILDREN_NUM 5
struct _CSNode
{
DataType data;
struct _CSNode *children[MAX_CHILDREN_NUM];
};
typedef struct _CSNode CSNode;
|
其中,子树的根节点的指针存放在 children 数组的前 k 个元素中,即如果 children[i] 的值为 NULL ,而 children[i-1] 不为 NULL ,则表明该结点只有 i 棵子树,子树根结点分别保存在 children[0] 至 children[i-1] 中。
队列相关定义及操作如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| struct __Queue
{
int i, j;
void **array;
};
typedef struct __Queue Queue;
Queue* create_queue();
bool is_empty_queue(Queue *tree);
void* del_queue(Queue *tree);
void add_queue(Queue *tree, void *node);
void free_queue(Queue *tree);
|
transform 函数定义如下:
1
| BiTNode* transform(CSNode *root);
|
其中 root 为普通树的根结点,函数返回该树对应二叉树的根结点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "bitree.h"
BiTNode *transform(CSNode *root)
{
if (!root)
return NULL;
BiTree biTree = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
biTree->data = root->data;
biTree->left = biTree->right = NULL;
Queue *queue = create_queue();
Queue *BiQueue = create_queue();
add_queue(queue, root);
add_queue(BiQueue, biTree);
while (!is_empty_queue(queue))
{
CSNode *csNode = del_queue(queue);
BiTree biNode = del_queue(BiQueue);
BiTree biPtr = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_CHILDREN_NUM; i++)
{
if (csNode->children[i])
{
BiTree newBiNode = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
newBiNode->data = csNode->children[i]->data;
newBiNode->left = newBiNode->right = NULL;
if (i == 0)
(biNode)->left = newBiNode;
else
(biPtr)->right = newBiNode;
biPtr = newBiNode;
add_queue(queue, csNode->children[i]);
add_queue(BiQueue, newBiNode);
}
}
}
free_queue(queue);
free_queue(BiQueue);
return biTree;
}
|
数组广义表
十字链表
十字链表相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct OLNode
{
int row,col;
ElemType value;
struct OLNode *right,*down;
}OLNode,*OLink;
typedef struct
{
OLink *rowhead,*colhead;
int rows,cols,nums;
}CrossList, *PCrossList;
|
实现十字链表的初始化操作:
1
| int init_cross_list(PCrossList L, const ElemType *A, int m, int n);
|
其中 L 指向 CrossList 结构,且各成员已被初始化为 0 ;
A 为 ElemType 类型数组中第一个元素的地址,元素的个数为 m×n 个,按行优先存储(即 A[0] 为十字链表第 1 行第 1 列的元素;
A[1] 为第 1 行第 2 列的元素,A[n] 为第 2 行第 1 列的元素,A[n+1] 为第 2 行第 2 个元素);
m 表示十字链表的行数,n 表示十字链表的列数。
init_cross_list 函数将 ElemType 数组中非 0 元素保存到十字链表中,函数返回非 0 元素的个数。
实现十字链表的删除操作:
1
| int del_cross_list(PCrossList L, ElemType k);
|
其中 L 指向 要处理的 CrossList 结构,k 为要删除的元素;
del_cross_list 函数删除十字链表中所有值为 k 的结点,并返回删除结点的个数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "crosslist.h"
int init_cross_list(PCrossList L, const ElemType *A, int m, int n)
{
L->rows = m;
L->cols = n;
L->nums = 0;
L->rowhead = (OLink *)calloc(m, sizeof(OLink));
L->colhead = (OLink *)calloc(n, sizeof(OLink));
OLNode *rowPtr = NULL,
*colPtr = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (A[i * n + j] != 0)
{
OLNode *olNode = (OLNode *)malloc(sizeof(OLNode));
if (olNode == NULL)
return -1;
olNode->row = i + 1;
olNode->col = j + 1;
olNode->value = A[i * n + j];
olNode->right = NULL;
olNode->down = NULL;
if (L->rowhead[i] == NULL)
{
olNode->right = L->rowhead[i];
L->rowhead[i] = olNode;
}
else
{
rowPtr = L->rowhead[i];
while (rowPtr->right)
rowPtr = rowPtr->right;
olNode->right = NULL;
rowPtr->right = olNode;
}
if (L->colhead[j] == NULL)
{
olNode->down = L->colhead[j];
L->colhead[j] = olNode;
}
else
{
colPtr = L->colhead[j];
while (colPtr->down)
colPtr = colPtr->down;
olNode->down = NULL;
colPtr->down = olNode;
}
L->nums++;
}
}
}
return L->nums;
}
int del_cross_list(PCrossList L, ElemType k)
{
OLNode *temp = NULL, *prev = NULL;
int delCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < L->rows; i++)
{
prev = NULL;
OLNode *rowPtr = L->rowhead[i];
while (rowPtr)
{
if (rowPtr->value == k)
{
if (prev == NULL)
L->rowhead[i] = rowPtr->right;
else
prev->right = rowPtr->right;
rowPtr = rowPtr->right;
}
else
{
prev = rowPtr;
rowPtr = rowPtr->right;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < L->cols; i++)
{
prev = NULL;
OLNode *colPtr = L->colhead[i];
while (colPtr)
{
if (colPtr->value == k)
{
if (prev == NULL)
L->colhead[i] = colPtr->down;
else
prev->down = colPtr->down;
temp = colPtr;
colPtr = colPtr->down;
free(temp);
L->nums--;
delCnt++;
}
else
{
prev = colPtr;
colPtr = colPtr->down;
}
}
}
return delCnt;
}
|
矩阵加法
实现三元组表示的两个稀疏矩阵的加法。相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| #define MAXSIZE 100
typedef struct {
int i,j;
ElemType e;
}Triple;
typedef struct {
Triple data[MAXSIZE];
int m, n, len;
}TSMatrix;
|
在三元组中,i 和 j 从 1 开始计数,与数学中矩阵元素的编号一致
矩阵加法函数的原型为:
1
| bool add_matrix(const TSMatrix *pM, const TSMatrix *pN, TSMatrix *pQ);
|
pM, pN, pQ 分别指向三个矩阵,当 pM 和 pN 两个矩阵不可加时,函数返回 false,否则函数返回 true,且 pQ 指向两个矩阵的和。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tsmatrix.h"
bool add_matrix(const TSMatrix *pM, const TSMatrix *pN, TSMatrix *pQ)
{
if ((pM->m != pN->m) || pM->n != pN->n)
return false;
pQ->m = pM->m;
pQ->n = pM->n;
pQ->len = 0;
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < pM->len && j < pN->len)
{
if ((pM->data[i].i < pN->data[j].i) || (pM->data[i].i == pN->data[j].i && pM->data[i].j < pN->data[j].j))
pQ->data[k++] = pM->data[i++];
else if ((pM->data[i].i > pN->data[j].i) || (pM->data[i].i == pN->data[j].i && pM->data[i].j > pN->data[j].j))
pQ->data[k++] = pN->data[j++];
else
{
pQ->data[k] = pM->data[i];
pQ->data[k].e = pM->data[i].e + pN->data[j].e;
if (pQ->data[k].e)
k++;
i++;
j++;
}
}
while (i < pM->len)
pQ->data[k++] = pM->data[i++];
while (j < pN->len)
pQ->data[k++] = pN->data[j++];
pQ->len = k;
return true;
}
|
查找
哈希表创建
哈希表( Hash Table,也叫散列表),是根据键( Key )而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。
也就是说,它通过计算一个关于键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,这加快了查找速度。
这个映射函数称做哈希函数,存放记录的数组称做哈希表。
哈希表相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| typedef enum{
HASH_OK,
HASH_ERROR,
HASH_ADDED,
HASH_REPLACED_VALUE,
HASH_ALREADY_ADDED,
HASH_DELETED,
HASH_NOT_FOUND,
} HASH_RESULT;
typedef struct __HashEntry HashEntry;
struct __HashEntry{
union{
char *str_value;
double dbl_value;
int int_value;
} key;
union{
char *str_value;
double dbl_value;
int int_value;
long long_value;
void *ptr_value;
} value;
HashEntry *next;
};
struct __HashTable{
HashEntry **bucket;
int size;
HASH_RESULT last_error;
};
typedef struct __HashTable HashTable;
HashTable *create_hash(int hash_size);
|
哈希表相关说明:
- HASH_RESULT 类型为相关函数的返回类型
- HashEntry 为哈希表所保存元素(即键值对 《key, value》)类型
- HashTable 为哈希表,其中 bucket 指向大小为 size 的、元素类型为 HashEntry* 的指针数组
- 哈希表采用链地址法处理冲突
请实现 create_hash 函数,创建指定大小的哈希表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "hash.h"
HashTable *create_hash(int size)
{
HashTable *table = (HashTable *)malloc(sizeof(HashTable));
if (table == NULL)
return NULL;
memset(table, 0, sizeof(HashTable));
table->bucket = (HashEntry **)malloc(sizeof(HashEntry *) * size);
if (table->bucket == NULL)
{
free(table);
return NULL;
}
table->size = size;
memset(table->bucket, 0, sizeof(HashEntry *) * size);
return table;
}
|
哈希表添加
哈希表( Hash Table,也叫散列表),是根据键( Key )而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。
也就是说,它通过计算一个关于键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,这加快了查找速度。
这个映射函数称做哈希函数,存放记录的数组称做哈希表。
哈希表相关定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| typedef enum{
HASH_OK,
HASH_ERROR,
HASH_ADDED,
HASH_REPLACED_VALUE,
HASH_ALREADY_ADDED,
HASH_DELETED,
HASH_NOT_FOUND,
} HASH_RESULT;
typedef struct __HashEntry HashEntry;
struct __HashEntry{
union{
char *str_value;
double dbl_value;
int int_value;
} key;
union{
char *str_value;
double dbl_value;
int int_value;
long long_value;
void *ptr_value;
} value;
HashEntry *next;
};
struct __HashTable{
HashEntry **bucket;
int size;
HASH_RESULT last_error;
};
typedef struct __HashTable HashTable;
HASH_RESULT hash_add_int(HashTable * table, const char * key, int value);
|
哈希表相关说明:
- HASH_RESULT 类型为相关函数的返回类型
- HashEntry 为哈希表所保存元素(即键值对 《key, value》)类型
- HashTable 为哈希表,其中 bucket 指向大小为 size 的、元素类型为 HashEntry* 的指针数组
- 哈希表采用链地址法处理冲突
请实现 hash_add_int 函数,向哈希表中添加元素,其中键类型为 char* , 元素类型为 int 。在添加过程中,如果要添加的键值 key 已在哈希表中,且对应的值 value 也已存在,则函数返回 HASH_ALREADY_ADDED ;如果要添加的键值 key 已在哈希表中,但对应的值 value 不同,则函数将 value 值更新到哈希表中,之后返回 HASH_REPLACED_VALUE ;如果要添加的键值 key 不在哈希表中,则函数创建 HashEntry 类型,并将其加入到哈希表中,且函数返回 HASH_ADDED。
本题所用的哈希函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| long hash_string(const char *str)
{
long hash = 5381;
int c;
while (c = *str++)
hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + c;
if(hash < 0)
hash *= -1;
return hash;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| #include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "hash.h"
#include <string.h>
HASH_RESULT hash_add_int(HashTable *table, const char *key, int value)
{
long hash = hash_string(key);
int index = hash % table->size;
HashEntry *hashPtr = table->bucket[index];
while (hashPtr)
{
if (strcmp(hashPtr->key.str_value, key) == 0)
{
if (hashPtr->value.int_value == value)
return HASH_ALREADY_ADDED;
else
{
hashPtr->value.int_value = value;
return HASH_REPLACED_VALUE;
}
}
hashPtr = hashPtr->next;
}
HashEntry *newEntry = (HashEntry *)malloc(sizeof(HashEntry));
if (newEntry == NULL)
{
table->last_error = HASH_ERROR;
return HASH_ERROR;
}
newEntry->key.str_value = strdup(key);
newEntry->value.int_value = value;
newEntry->next = table->bucket[index];
table->bucket[index] = newEntry;
return HASH_ADDED;
}
|
AVL添加
平衡二叉树,是一种二叉排序树,其中每个结点的左子树和右子树的高度差至多等于 1 。它是一种高度平衡的二叉排序树。
现二叉平衡树结点定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| typedef struct node
{
int val;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
struct node *parent;
int height;
} node_t;
|
请实现平衡二叉树的插入算法:
1
2
|
node_t *avl_insert(node_t *root, int val);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "avl.h"
#define max(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b))
int get_height(node_t *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return 1 + max(get_height(root->left), get_height(root->right));
}
int get_balance_factor(node_t *root)
{
return get_height(root->left) - get_height(root->right);
}
node_t *right_rotate(node_t *y)
{
node_t *x = y->left;
y->left = x->right;
x->right = y;
y->parent = x;
if (y->left != NULL)
y->left->parent = y;
y->height = get_height(y);
x->height = get_height(x);
return x;
}
node_t *left_rotate(node_t *y)
{
node_t *x = y->right;
y->right = x->left;
x->left = y;
y->parent = x;
if (y->right != NULL)
y->right->parent = y;
y->height = get_height(y);
x->height = get_height(x);
return x;
}
node_t *avl_insert(node_t *root, int val)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
node_t *newNode = (node_t *)malloc(sizeof(node_t));
newNode->val = val;
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
newNode->parent = NULL;
newNode->height = 1;
return newNode;
}
if (val < root->val)
{
root->left = avl_insert(root->left, val);
root->left->parent = root;
}
else if (val > root->val)
{
root->right = avl_insert(root->right, val);
root->right->parent = root;
}
else
{
return root;
}
root->height = get_height(root);
int bf = get_balance_factor(root);
if (bf > 1 && val < root->left->val)
return right_rotate(root);
if (bf > 1 && val > root->left->val)
{
root->left = left_rotate(root->left);
return right_rotate(root);
}
if (bf < -1 && val > root->right->val)
return left_rotate(root);
if (bf < -1 && val < root->right->val)
{
root->right = right_rotate(root->right);
return left_rotate(root);
}
return root;
}
|
,其缩进形式为:
。